[ESG Management and Practice] How Can a Bank Become an ESG Leader in Mainland China?
Source: WeChat official account “New Wealth”
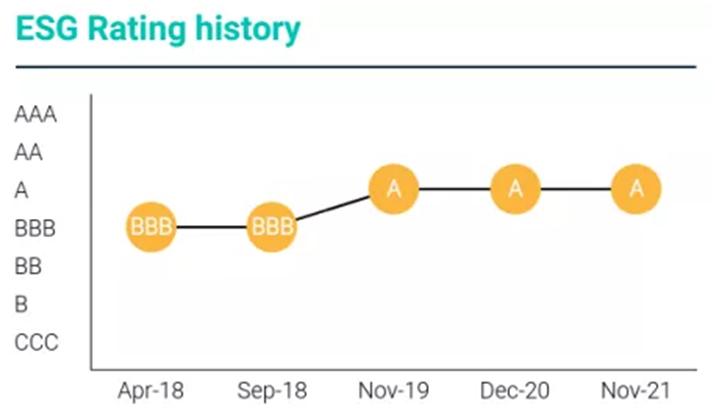
For three consecutive years, IB has been maintaining the highest rating of MSCI domestic banking industry. IB is the forerunner and outstanding representative of ESG practice in the banking industry of mainland China, who has won domestic and international recognitions through accumulated experience and achievements for nearly 19 years. In the MSCI ESG rating, IB has been rated A for three consecutive years, which represents the highest level in the domestic banking industry and is also the only banking institution in the mainland China with Rating A for three consecutive years.
In the E-Dimension, IB takes the lead in green finance and explores the carbon-related financial market. IB, as a pioneer of green finance, is the first bank in China that has adopted the Equator Principles. Since 2006, it has been “planting green” finance for 16 years, forming a green product system with complete categories and rich varieties, who is the largest commercial financial institution in the world for issuing and underwriting green financial bonds.
In the S-Dimension, IB adjusts measures to local conditions to create differentiated samples. In terms of social responsibility, financial institutions in China focus on such issues as employee training, community service, inclusive finance, targeted poverty alleviation, public welfare and charity. As a national joint-stock bank, IB combines the first-mover advantage of green finance, makes use of financial technology to actively develop inclusive finance, and forms a long-term three-in-one assistance mechanism of “donation for education”, “disaster relief” and “poverty alleviation”, which provide financial services with love and has embarked on a practice road of featured social responsibility of “combining social responsibility with corporate interests”.
In the G-Dimension, IB’s top-level strategic escort is incorporated into its development plan, which attached importance to two-way high-quality communication of information disclosure. The ESG practice of commercial banks not only includes improvement of governance and organizational structure, such as the establishment of an ESG committee, dedicated officials or teams to ensure the implementation of relevant work, but also covers high-quality information disclosure and two-way communication with stakeholders. IB took the ESG management as an important part of the company’s top-level strategy at an early date, and continuously disclosed ESG information to the public for 13 consecutive years.
01
Foreword
Along with the transformation of domestic economic growth model and the steady progress of the double carbon-related (carbon peaking and carbon neutrality) strategy, the ESG concept with environmental, social and corporate governance as its core has been highly valued by all sectors of the society. ESG is a widely adopted international standard for judging sustainable development capability, which is also an important starting point for China to implement the double carbon-related (carbon peaking and carbon neutrality) target.
Financial institutions are an important force in practicing the ESG concept, in particular, the commercial banks, as an important part of the financial system, who should attach importance to the ESG aspect, and practicing the ESG is of great and positive significance to the whole economic and social development in a state. First of all, under the background of active global response to climate change, the ESG practice is conducive to accelerating the sustainable development and transformation of the banking industry, and tapping the opportunities of green and low-carbon market; Second, the practice of ESG principles by banking and financial institutions is helpful in better adaptting to the trend of industrial supervision. In 2020, for example, the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission proposed the ESG management as a universal principle for high-quality development of banking industry, and in 2021, the ESG was explicitly incorporated into the business process of financial institutions. Third, incorporating the ESG concept into the daily operations will help commercial banks to operate more steadily and regulate corporate governance, and attract the attention of mainstream investment institutions.
IB is one of the pioneers in practicing the ESG in the banking industry of mainland China, whose achievements have been widely recognized at home and abroad, and therefore, its ESG performance has been rated A by Morgan Stanley Capital International (MSCI), an international authority, for three consecutive years. Through the research and analysis of IB ESG, we may provide reference for the industry, from which we can note that the domestic banking industry is gradually improving its relationship with stakeholders, promoting social development and truly becoming an outstanding corporate citizen by virtue of its active practitioner status of the sustainable development concept.
02
Overview of IB ESG
Overview of the ESG information disclosure & ESG rating and index inclusion
IB (601166.SH) ESG has a high degree of transparency in information disclosure. After the Company first released the 2008 Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Report, the 2009 CSR Report was renamed as the Sustainable Development Report in order to better practice the concept of sustainable development. Through the disclosure of ESG information for 13 consecutive years, IB has conveyed to the public its commitments, actions and progress in fulfilling its social responsibility and promoting sustainable development, and has truly and objectively recorded important information in fulfilling the concept of sustainable development and creating environmental and social values during the reporting period.
Among more than 40 A-share listed companies affiliated to the banking industry, the IB ESG performance is at the upstream level of the industry both at home and abroad. Internationally, the IB was upgraded from “BBB” by MSCI ESG rating to “A” in 2019 and continuously remained rating “A” in 2020 and 2021. In FTSE Russell’s latest rating, IB ranked first in the industry with a score of 2.3 (out of a total of 5 points, with an industry average score of 1.81).
At present, there are more than 100 ESG subject indexes in mainland China, and IB has been included in the sample stock by the domestic mainstream ESG indexes such as SSE 50 ESG benchmark index, SSE 180 ESG leading index, Shanghai and Shenzhen 300 ESG leading index and CSI 180 ESG value index.
|
Chart 1: Inclusion of IB in the Major ESG Indexes in Mainland China |
|
|
Name and Code of Inclusion Index |
Inclusion Weight |
|
SSE 50 ESG Benchmark Index (950223.CSI) |
4.06% 4.06% |
|
Shanghai and Shenzhen 300 ESG Benchmark Index (931463.CSI) |
3.31% 3.31% |
|
CSI 180 ESG Index (931088.CSI) |
2.66% 2.66% |
|
CSI 800 ESG Leading (931651. CSI) |
2.56% 2.56% |
|
SSE 180 ESG Leading (950226.CSI) |
4.86% 4.86% |
|
Source: WIND, Securities Times CMR |
|
03
IB Maintains MSCI Highest Rating of Banking Industry in Mainland China for Three Consecutive Years.
As a pioneer in the practice of ESG concept in mainland China, the Industrial Bank (IB) (SH.601166) has been continuously integrating the ESG concept into its development in recent 19 years, which has accumulated rich ESG-related experience and achievements, and gained the recognitions at home and abroad.
In the 2021 ESG rating by an international authority MSCI, IB was rated A, the highest level in the banking industry of mainland China, becoming the only banking institution in the domestic banking industry with rating A for three consecutive years. In 2021, IB was awarded the Most Valuable Bank by the Banker, a British magazine, who previously awarded IB such titles as the Best Green Bank and the Best Private Bank.
Since 2018, IB has been awarded the title of Advanced Entity in the Overall Evaluation of Green Bank for two consecutive years in the domestic green bank rating activities under the guidance of the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission. IB is also an active promoter of the ESG concept, advocating the parallel of “intelligence” and “financing”, and has participated in the revision and formulation of a number of domestic and foreign green finance policies.
By the end of 2021, the IB’s market value exceeded RMB 400 billion, ranking No. 7 among those listed companies in the banking industry of mainland China, with total assets of RMB 8.6 trillion, ranking No. 8 nationwide. In 2021, IB’s annual operating revenue was RMB 221.236 billion, with an increase of 8.91% compared with the previous year, whose net profit reached RMB 82.68 billion, with an increase of 24.10% compared with the previous year.
In brief, IB, born in Fuzhou, a coastal city in southeast China, has developed itself from a local bank to a large national commercial bank in China within since its establishment more than 30 years ago, who takes the lead in terms of comprehensive strength and becomes the leader of Chinese joint-stock commercial banks.
04
ESG Practice Originated from the “Equator Principles”
The IB’s consciousness of sustainable development started from Xi Jinping’s important instructions and earnest teachings on the construction of ecological civilization in Fujian Province during his working period there. As a national joint-stock bank born in and developed in Fujian Province, IB has always been carrying forward the important concept and major practice in the construction of ecological civilization when Xi Jinping worked in Fujian Province, closely combining with the idea of learning, understanding and practicing Xi Jinping ecological civilization, always guiding its operation and development with Xi Jinping’s idea of ecological civilization, and constantly exploring the ways for financial reforms with the specific action and actual effect of constructing ecological civilization, so as to maintain the original mission of making contributions to economic development.
In 2003, as a result of appreciating and preferring the service goal of “promoting the sustainability of developing member countries” proposed by the International Finance Corporation (IFC), IB introduced the IFC as its important strategic investor, and arranged two environmental protection officials to take charge of the bank-wide environmental and social compliance management, which is also the origin of IB’s ESG practice. In 2006, during the process of launching the first domestic energy efficiency financing project for sustainable financial standardization products by cooperating with the IFC, IB gradually realized the importance of environmental factors for daily loan approval, thus beginning the exploration of the Equator Principles in its sustainable development.
Since then, IB has been actively carrying out exchanges with domestic and foreign banks. Through multiple demonstrations on the business impact, risk response strategies, business structure, as well as the impact of profit model, IB believes that the Equator Principles are highly consistent with its own development philosophy and long-term interests, which is also in line with the strategic objectives of the Bank’s transformation and development. In 2008, IB officially announced the adoption of Equator Principles, becoming the first “crab eater” in China’s banking industry.
The EPFI refers to a bank that adopts Equator Principles and promises to use Equator Principles in financing services for the management of financing projects. Non-financial factors including the environment, society and corporate governance are the evaluation points of Equator Principles. The core elements of Equator Principles are basically consistent with the ESG concept, which all aim to achieve the goal of sustainable development.
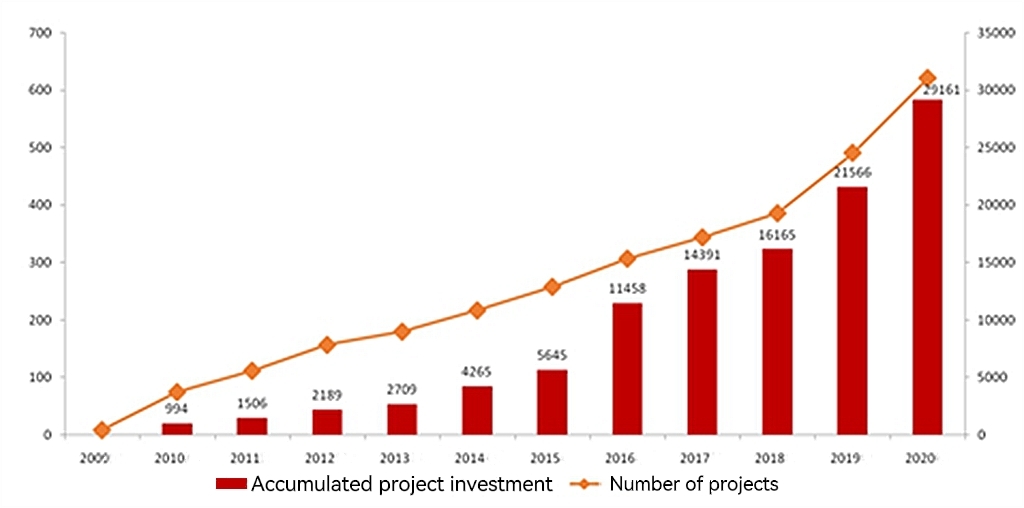
Since IB adopted the Equator Principles in 2008, the amount of its project investment that adheres to the Equator Principles has been increased rapidly. As of the third quarter of 2021, IB has reviewed 1,488 projects on the applicability of Equator Principles, and applied the Equator Principles in 815 projects with a total investment of RMB 3.54 trillion. In terms of the growth trend, it took IB seven years for the accumulated project investment amount to reach the first trillion, reaching RMB 1.15 trillion by 2016, and three years to reach the second trillion, namely, the increase from RMB 1 trillion to RMB 2 trillion during 2017-2019. Moreover, IB accelerated its development speed again in 2020, reaching RMB 3 trillion compared with the previous year in the projects that applied Equator Principles.
In 2007, Robert Zoellick, the then President of the World Bank, asked IB, “If the money can be earned through green finance, why don’t other Chinese banks engage in such business? If not, why do you do it?” IB representative answered: “Maybe we will not make money in a short term, or even take some risks, but we need support the cause of environmental protection. Banks can give play to their own strengths and support the cause of environmental protection through credit leverage. With the joint cultivation of all stakeholders, there will be a market and profits sooner or later, which will achieve an effective combination of bank operating activities and fulfillment of corporate social responsibilities.”.
According to IB, the practice of Equator Principles is beneficial to improve a bank’s risk control capacity. First of all, the Equator Principles require to incorporate the environmental and social risk management into business processes, which is advantageous for the bank to select the business in a more scientific and reasonable manner, thus eliminating or resolving projects with potential risk.
Second, IB has carried out cost estimation internally at the initial stage of putting into effect the Equator Principles, and the implementation of such principles will not increase the bank’s operating costs, which has paved the way for business promotion.
Third, the projects reviewed under the Equator Principles are characterized with low risks and stable long-term benefits. According to the statistics of the People’s Bank of China, the non-performing rate of green credit in China was only 0.73% by the end of 2019, and the non-performing rate of all loans in the same period was 1.86%. A large number of special studies conducted in the domestic and foreign academic circles have shown that the higher the ESG rating level, the more stable the long-term corporate financial performance.
Years of practice have confirmed the accuracy of IB’s judgment, and green finance has become one of the three key IB golden business cards, bringing both social and commercial benefits to the Bank. While having achieved fruitful results, IB always remembers to share the excellent experience and innovative practices with it stakeholders. It extensively exchanges the standards, technologies and experience formed in the best practice of localizing the Equator Principles with international communities through multilateral cooperation platforms to contribute Chinese wisdoms, and maintains positive interactions with banks of the emerging market countries such as Vietnam, Thailand, and Mongolia.
05
E-dimension
From the ESG experience at home and abroad, the environmental dimension is the most concerned issue, and financial institutions mainly implement such dimension through the development of their green finance and low-carbon banking operation. As a pioneer in green finance, IB has been carrying out the “planting green” finance for 16 years and formed a complete and diverse green finance product system since 2006, which is a commercial financial institution with the largest scale of green finance bond issuance and underwriting in the world. In terms of its own operations, IB also follows the guidelines of energy conservation and environmental protection, and minimizes the negative environment effect from daily operation and supply chain procurement.
Taking the Lead in the Green Credit Growth
Green credit is currently the largest variety in the domestic green finance market. After the cultivation for more than ten years, IB has established its leading institutions and teams in China’s banking industry, and built a series of professional green finance operating systems. IB’s growth rate and relative scale of green credit ranks top among the banks of mainland China.
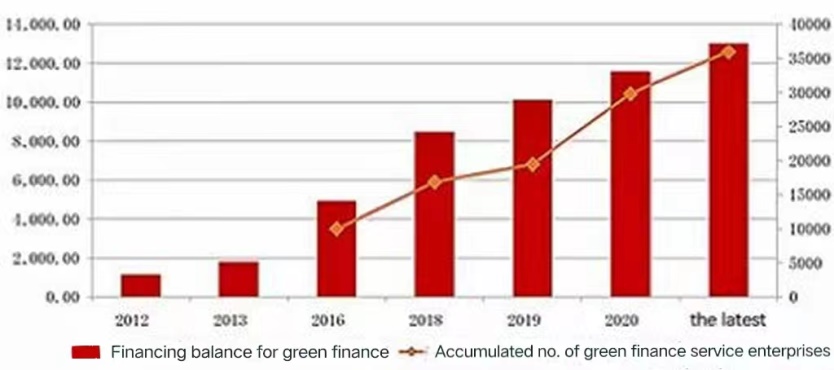
As of the end of 2021, the IB’s balance of on- and off-balance sheet for green finance has reached RMB 1.39 trillion, with an increase of 19.98% from the beginning of the period, while its number of green finance customers reached 38,000, with an increase of 29.92% from the beginning of the period, among which the green loans through the People’s Bank of China are increased by 42.10% to RMB 453.94 billion from the beginning of the period. The supported projects are expected to save 40.88 million tons of standard coal and reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 106.72 million tons annually in China.
Compared with the data in 2012, IB’s green financing balance has been increased from RMB 112.6 billion to nearly RMB 1.4 trillion within the recent nine years, with a substantial growth of 12 times; and the number of enterprises under service has been developed from about 1,700 to 38,000, with an increase of more than 20 times.
According to IB, Chinese banks are driven by policy factors in 2021, and the scale of domestic green loans gains its momentum. IB will leverage its advantages in green finance, continue to make efforts in achieving the “carbon peaking and carbon neutrality” goal, and increase support to clients in such industries as clean energy. IB’s green credit growth is taking a leading position in mainland China in 2021. In terms of the scale of green loans among the total bank loans, IB ranks top in the market with a ratio of 9.8%.
While increasing the investment in green credit, IB continues to reduce the scale of investment in “brown” assets, and implements a differentiated credit policy of “guarantee, control and reduction” for industries with excess capacity such as the steel, coal, and non-ferrous metals sectors. During 2018 and 2020, IB’s loan balances for industries with “two highs (high energy consumption and high pollution) and one surplus (having excess capacity)” were RMB 65.282 billion, RMB 47.547 billion, and RMB 51.999 billion in turn, accounting for 3.9%, 2.73%, and 2.62% of total corporate loans respectively, with a gradual decrease year by year.
Ranking First in Green Bond Issuance and Underwriting
Green bonds are products that are second only to credit in the green finance market. IB also ranks top among domestic companies in terms of issuance and underwriting. By the end of 2021, IB has issued green finance bonds.at a total amount of RMB 130 billion. In the meanwhile, It takes the initiative of the “commercial bank + investment bank” model to increase green bond investment and transactions, and deeply participates in Chins’ green bond market. In 2021, IB underwrote the green bonds for more than RMB 30 billion, ranking No. 1 among the joint-stock banks in mainland China for five consecutive years.
Apart from the advantages of scale, IB has actively innovated in the varieties of green bonds, creating the practice of several “No. 1” in China’s banking industry. In 2016, the Bank issued green finance bonds at the amount of RMB 50 billion in the domestic market for the first time. In November 2018, IB issued the first overseas green finance bonds and two varieties of USD 600 million and EUR 300 million in the same period, who is the first bank in mainland China to complete the issuance of green finance bonds in both domestic and overseas markets. At the same time, it signed a strategic cooperation agreement with the Luxembourg Stock Exchange which brings together more than 50% of the world's green bonds.
Facing the pandemic situation in 2020, IB underwrote the first “green epidemic prevention bond” in the market. In the same year, it issued overseas blue bonds in Hong Kong and underwrote the first corporate blue bond in mainland China, who provided references for domestic and foreign institutions in exploring blue bond standards, and became the first domestic institution to sign the United Nations Sustainable Blue Economy Finance Initiative. As a type of green bond, blue bonds are dedicated to a sustainable marine economy and play an important role in promoting marine protection and sustainable utilization of marine resources.
Exploration of the Carbon Finance Market
IB leverages the advantages of a green finance group to enrich the variety of ESG investments at home and abroad from both the supply and demand sides. On the supply side, in addition to green loans and bonds, IB has introduced innovative green finance products and services such as “environmental protection loans” “water-saving loans” “green ticket pass” and “green innovation loans”. This does not only effectively alleviate the problems on lack of pledges and collaterals, financing difficulties, and expensive financing in the process of green transformation and development of enterprises, but also helps to enhance the guiding and leveraging role of government special green funds.
At the other end, IB works in coordination with its subsidiaries such as Industrial Trust, Industrial Fund, and IB Wealth Management to form a series of ESG products covering green trust, green public fund and ESG wealth management, providing a convenient channel for small and medium-size investors to participate in green investment. The wholly-owned subsidiary, IB Wealth Management, is one of the first bank wealth management subsidiaries in China to launch ESG-themed products. From September 2020, when the first net-worth green-themed wealth management product “IB ESG Beautiful China No. 1” was issued, to October 2018, when the Company launched the first hybrid ESG wealth management product “ESG Promoting Green Development”, IB has issued a total of 7 green-themed wealth management products.
IB is also one of the earliest banks to explore carbon finance services in China. It began to deploy carbon finance services as early as 2007, and has successively launched the first agreed repurchase financing project with long-term carbon sink products as the target, and the first batch of carbon financing projects in China. IB also issued the first batch of carbon neutral bonds, the first equity-funded carbon neutral bonds, and the first batch of bonds linked to sustainable development in China. IB takes the lead in the domestic banking industry to adopt the United Nations Convention on Climate Change “CLIMATE NEUTRAL NOW” initiative. In order to contribute to the carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goal IB has not only determined its own operational carbon neutrality goal and roadmap, but also explored use of such technologies as the big data, Internet of Things, block chain to monitor and manage itself and service enterprises, the project’s carbon emission and carbon footprint so as to improve its ESG management capacity.
Empowering the Digital Green Finance
Financial technology can reduce costs and improve efficiency, which is an important step for financial institutions to carry out digital transformation. IB organically combines the advantages of science and technology with those of green finance, and actively explores a new path for the ESG to help achieve the “carbon peaking and carbon neutrality” goal. IB has updated its self-developed green finance technology system for the third time, gradually integrated such functions as product research and development, external data integration, processing, application, peer cooperation, with the functions such as communicating with cooperation platforms between customers and governments.
In addition, the system of “from Green to Gold” developed by IB may accurately calculate the environmental benefits of dozens of industries related to low-carbon economy, circular economy and ecological economy through the integrated application of cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data, which may accurately analyze and evaluate the social and environmental risks of enterprises applying for loans, and become an industry-leading IT support platform of collectivization for green finance business.
Sustainable Development of Green Operation
The green operation of the bank itself is also an important part of ESG practice. The common practice is to reduce energy consumption through such actions as green office and green procurement for the purpose of reducing damage to the environment.
IB integrates the concept of sustainable development into its daily work by promoting such means as water and electricity conservation, paperless office, online conference, green travel. Since 2013, IB has been carrying out the energy-saving transformation for office space, and reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions of its own operations by taking actions such as promoting use of LED lamps and building a precision air conditioning system in the machine room. In terms of the selection of supply chain enterprises, IB insists on reviewing supplier’ certification in such aspects as environmental protection, safety production and labor security during the procurement process, and takes suppliers’ environmental and social performance as the reference standard for the procurement.
It is worth mentioning that the IB Fuzhou Headquarters Building has obtained a two star certificate for green building design identification, making itself to be a modern building model of low-carbon environmental protection and green development, who has taken its due responsibility for the improvement of natural environment.
S-dimension
In terms of social responsibility, financial institutions in mainland China focus on such issues as employee training, community service, inclusive finance, targeted poverty alleviation and charity. There is little difference in the work of various banks in this regard, and the large state-owned banks have obvious advantages in the scale of capital investment, while IB has taken a differentiated road by combining the first-mover advantage of green finance.
Inclusive finance helps the development of the real economy
As a joint-equity bank in China, IB is the first one to set up an inclusive finance division. By comprehensively using group resources and diversified financial instruments, it has continuously expanded the scope of inclusive finance such as bank-bank cooperation, pension finance, small and micro finance, finance on agriculture, rural areas and farmers. The main characteristics of IB’s related business are as follows.
1. IB continues to increaseits credit support to small and micro enterprises, and expands its loan scale and service coverage steadily. By the end of 2021, the loanbalance of inclusive finance for small and micro enterprises was RMB 298.8 billion, with an increase of RMB 107.5 billion and with a growth rate of 56% compared with the beginning of the year; the number of inclusive small and micro loan households exceeded 150,000, an increase of 69% compared with the beginning of the year; and year-on-year growth of several indicators exceeded the domestic average.
2. IB continues to strengthen financial technology empowerment and explores newinclusive finance models, such as small and micro-finance and rural finance through leveraging such open platforms as the Bank-bank Platform, the “Financial Services Cloud Platform”of Fujian Province and IB Inclusive Cloud Platform. IB’s self-developed “Financial Services Cloud Platform” accurately matches the financing demands of enterprises and financial products of banks, serves over 160,000 small and micro enterprises, and solves the financing demands of over RMB 100 billion. In the meanwhile, IB has been expanding the development and promotion of the small and micro online financing system, and integrating its online application scenarios in the production and operation links of small and micro enterprises such as “contract loan” “e-ticket loan” and “loan by car pledges”.
3. IB increases the scale of fee reduction, and has expanded the coverage of preferential services and provided “strong”fee reduction in accordance with the requirements of the Notice on Reducing the Payment Fees of Small and Micro Enterprises and Individual Industrial and Commercial Householdsjointly issued by the central bank, China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission and other two ministries, apart from providing “caring” payment services to small and micro enterprises and individual businessmen. In 2021, IB reduced fees at a total amount of about RMB 8.4 billion, of which the fee reduction of enterprises involved was about RMB 1.8 billion (including about RMB 400 million of fee reductions to support small and micro enterprises) and about RMB 6.6 billion of fee reductions and concessions for retail customers.
Exploring the way of targeted poverty alleviation with IB characteristics
Targeted poverty alleviation is the content of ESG practice with Chinese characteristics, which reflects the important contribution made by enterprises in undertaking their social responsibility. Financial institutions determine the allocation of social capital and are the main participants in poverty alleviation. IB, taking its advantage of green bank, has created a featured poverty alleviation path, who has been successively awarded the “Best Differentiated Targeted Poverty Alleviation Institution of the Year” in the First China Financial Value Ranking, and the “Targeted Poverty Alleviation Financial Institution of the Year” in the Asian Finance (Annual Conference) in the 21st Century.
IB adopts a differentiated and targeted approach to poverty alleviation by insisting on placing equal emphasis on both support and capacity generation. The management attaches great importance to poverty alleviation, and has set up a financial poverty alleviation leading group headed by the IB President to establish an internal coordination mechanism and formulate an overall implementation plan, so as to make the financial services more available in the poor areas. In terms of business, IB proposed “five poverty alleviation systems”, involving industrial poverty alleviation, channel poverty alleviation, product poverty alleviation, fixed-point poverty alleviation and education poverty alleviation. The industrial poverty alleviation aims to activate the function of “autologous hematopoiesis”, explore the modes of industrial poverty alleviation such as the “bank + leading enterprises + farmers”, and develop special financial products such as forest property mortgage loan, cattle rights loan and financial loan for small and micro clothing and waving enterprises. In terms of green poverty alleviation, IB has successively signed strategic cooperation agreements on green finance with stakeholders in such provinces or regions as Jiangxi, Guizhou, Xinjiang and Yunnan where there are a large proportion of poor people, and has cumulatively granted green financing at the amount of RMB 146.9 billion to help local poverty alleviation through the projects of improving local eco-environmental protection and optimizing agricultural product structure.
To consolidate and enlarge the achievements of poverty alleviation and the work of rural vitalization in parallel, IB issued the Guiding Opinions on Conducting the Work of Consolidating and Expanding the Achievements of Poverty Alleviation and Promoting the Work of Rural Vitalization Comprehensively in April 2021, and drew a “planning map” and “road map” of IB high-quality services to support rural revitalization, which aims to further enhance economic vitality and development potential of poverty-alleviation areas, further enhance the competitiveness of rural industries and basic public services, and continuously improve the rural ecological environment and living standards of low-income population. By the end of 2021, the balances of loans and inclusive loans related to the agriculture, countryside and farmers and of the loans for new-type agricultural entities were RMB 476.2 billion, RMB 27.8 billion and RMB 31.2 billion in turn, with an increase of 10.67%, nearly 80% and 14.47% respectively.
07
G-dimension
In terms of corporate governance, the ESG practice of commercial banks does not only include the improvement of corporate governance and organizational structure, such as the establishment of ESG committees, full-time officials or teams to ensure the implementation of relevant work, but also covers the high-quality information disclosure and the two-way communication with stakeholders. IB took the ESG management as an important part of its high-level strategy at an earlier stage, and continuously disclosed the ESG information for 13 consecutive years.
Incorporated ESG in the Bank’s development planning
The ESG practice involves multi-department collaboration, which requires the arrangement of corporate top-level system, so as to ensure its implementation in place. IB has made detailed arrangements from the top-level institutional design, studied and promoted the adjustment of the “Strategy Committee” of the Board of Directors to the “Strategy and ESG Committee”, supplemented the ESG-related responsibilities on the basis of the original Strategy Committee, who should be responsible for reviewing such matters as the corporate ESG strategies as well as environmental and social policies.
IB further reflects the importance of ESG-related work in its future development strategy. Through the research and interviews, it enhances the awareness of ESG concepts and sets feasible ESG goals, and its ESG strategic planning has gradually become matured, and the ESG strategic planning has been incorporated in the IB five-year plan (2021-2025). IB expects that the ESG management system and process will be gradually shaped in such aspects as corporate governance, product creation, investment decision-making, risk management, green operation and information disclosure.
Disclosure of ESG-related information for 13 consecutive years
High-quality information disclosure is an important part in practicing the ESG, which directly affects the bond issuance and refinancing of enterprises. Throughout the ESG information disclosed by IB for the 13 consecutive years, it has the following characteristics:
1. The IB’s disclosure standard is high. In addition to continuing to follow the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the information disclosure indicators of the Principles of Responsible Bankingand the GRI Sustainable Development Reporting Standard, IB further strengthens the ESG information disclosure in line with the mainstream ESG ratings in domestic and international markets, the TCFD framework and the ESG disclosure guidelines of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, andhas built a social responsibility system with 370 indicators in five categories.
2. IB pays attention to the two-way communication with stakeholders, and improves the ESG practice capacitybased on feedbacks. Such a two-way communication makes IB in the information disclosure more accurate and more conducive to information dissemination and reception. IB distributed questionnaires tomultiple stakeholders, including regulators, customers, residents and investors, to collect their opinions and suggestions on the key IB ESG-related issues, who collected about 30,000 questionnaires on average per year. The results of the questionnaires and the demands of relevant parties are decomposed into various IB departments accordingly, and effective improvement measures are formulated to promote the ESG management effectively.
3. IB sets up a multi-dimensional and multi-frequency independent disclosure system for different stakeholders. It includesthe Annual Reportfor all social audiences, the Annual Sustainable Development Report, the official website of IB, which is updated irregularly, and the semi-annual Social Responsibility Report: From Green to Gold for internal and regulatory departments.
In addition, IB hired a third-party agency to verify the data and information in the ESG reports in order to ensure the fairness of ESG data, which has greatly improved its credibility of the data, and reflected the Company’s confidence in its own ESG management. The IB’s ESG information disclosure has been recognized at home and abroad. At the 9th China-UK Economic and Financial Dialogue in 2017, IB participated in the pilot work of environmental information disclosure as one of the first 10 pilot financial institutions in mainland China.
08
Summary
In general, IB is an excellent representative of ESG practice in the banking industry of mainland China, who has been vigorously developing green finance at the environmental level and taking the leading position in a number of core business data. In terms of social responsibility, IB has been increasing support for financial inclusion and targeted poverty alleviation, and giving full play to its own advantages in the creation of differentiated samples. At the corporate governance level, IB’s senior management has been attaching great importance to the ESG practice strategically, adhering to the long-term high-quality disclosure of ESG information, and conducting the two-way high-quality communication with various stakeholders. At the same time, it should also be noted that the ESG practice in China’s banking industry started late whose foundation is weak, and there are still some shortcomings, such as the lack of unified standards or data information sharing, and the absence of unified ESG risk rating standards in the industry. Therefore, there is much room for the improvement in such aspects as the basic system and information disclosure.